Look around, and you will see that magnets are everywhere, from the phone or computer you are using to read this article to the door of your wardrobe. They are also present in electric motors and generators and the needle of compasses. Magnets are any material that exerts a magnetic force that attracts like poles while repelling un-like poles. Magnets are made of many different materials, most notably neodymium magnets.
Magnets possess different strengths; therefore, it is necessary to establish the power of a magnet to determine the use it is best suited for. The two major classifications are the N50 magnets and the N35 magnets. In this blog, we will discuss their properties and establish which of the two is the strongest. We will also look into magnet grading, testing magnet strength, and how to choose the most suitable magnet for yourself.
Understanding Magnet Grades
The grades of a magnet are the measure of its strength. The magnets are graded on the maximum force they can produce. As you have seen with N50 magnets and N35 magnets, the letter represents the material used to create the magnet. The letter ’N’ is used for magnets made with neodymium. Other materials, such as samarium cobalt and alnico, are also used to construct magnets.
The number that follows the letter is the measure of the actual strength of the magnet. To determine the strength, measurement is taken in Gauss, which is the unit that tells you much attractive force a magnet has. Another unit, the Oersted, is also measured, which tells you how permanent the attractive force of the magnet is.
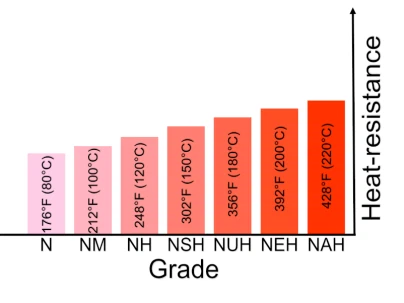
Both of these properties are important for a magnet. Therefore, we multiply these two units to get the maximum energy product, the Mega Gauss Oersteds (MGO). This is the number that is used to grade the magnet. Neodymium magnets are greatly affected by temperature causing significant variations in their performance. Letters for the temperature resistance are also added after the grade number.

How Do You Measure The Strength Of A Magnet?
The strength of a magnet can be measured using two different units. One is the pull force, while the other is the magnetic field strength.
| Goudsmit grade code | Remanence br | Normal coercivity HcB | Intrinsic coercivity HcJ | Maximum energy product (BH)max | Maximum operating temperature | ||
| minimum value | typical value | minimum value | minimum value | minimum value | typical value | T max | |
| (mT) | (mT) | (kA/m) | (kA/m) | (KJ/m³) | (KJ/m³) | (℃) | |
| N35 | 1170 | 1220 | 860 | 955 | 263 | 287 | 80 |
| N38 | 1220 | 1250 | 860 | 955 | 287 | 310 | 80 |
| N40 | 1250 | 1280 | 860 | 955 | 302 | 326 | 80 |
| N42 | 1280 | 1320 | 860 | 955 | 318 | 342 | 80 |
| N45 | 1320 | 1370 | 860 | 955 | 342 | 366 | 80 |
| N48 | 1370 | 1420 | 836 | 955 | 366 | 390 | 80 |
| N50 | 1390 | 1440 | 836 | 955 | 376 | 408 | 80 |
| N52 | 1420 | 1470 | 836 | 876 | 390 | 421 | 80 |
| N54 | 1450 | 1500 | 836 | 876 | 406 | 438 | 80 |
· Pull Force
The pull force is the amount of power necessary to pull the magnet away from something, whether a metal surface or another magnet. It is usually measured in pounds but also in kilograms and newtons.
· Magnetic Field Strength
The magnetic field strength is the amount of magnetic force applied to an object in the presence of magnetic fields. The measurement is taken in Gauss. Magnetic flux density is also related to magnetic field strength, a measure of how much magnetic field passes through a particular part of a surface. The unit for this measurement is Tesla.
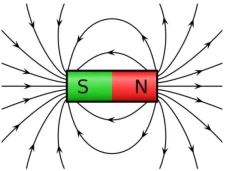
· Pull Force Test
The complete surface of the magnetic assembly is examined using a half an inch thick plate of steel. Starting from a clean steel and magnet surface, you place the magnet in the center of the steel plate. The assembly is then attached to a hook connected to a measuring device such as a dynamometer. The machine pulls the magnet away very slowly until enough force is applied to break the magnet away from the steel plate. This represents the breakaway force.

· Magnetic Field Measurement
A Gaussmeter is used to measure magnetic field strength. Before measuring the field strength of any magnet, it is crucial to ensure that there aren’t any other magnetic objects in the area where you are taking the measurement. You then put the Gaussmeter on one of the poles of the magnet. The needle will show the reading of the field strength.
· Magnetometer
A Magnetometer is another type of Gaussmeter to measure the field strength. Some magnetometers also have Hall effect sensors for detecting any voltage created by introducing a semiconductor with current flowing through it into the magnetic field.
N50 Magnets: Unleashing The Powerhouse
A type of magnet made from rare earth-metal neodymium, the N50 magnets are considered one of the strongest magnets on the market. The N50 grading is a marker of its high strength, as N50 magnets have a very high maximum energy product. The average power of an N50 magnet is from 48 to 52 MGOs.
· Characteristics
The N50 magnets have multiple features that set them apart from other magnets. Among the strongest permanent magnets, they can create a tremendous magnetic force to create formidable magnetic fields. This makes it very easy for them to attract magnetic materials. The N50 magnets also have a much more compact size when compared to magnets that have similar power. This makes them ideal for use in areas with little space.
The capacity of a magnet to matin the strength of its magnetic field over time is called its remanence. The N50 magnets have a very high remanence allowing them to maintain their magnetic force over very long periods. The magnets are also incredibly resistant to demagnetization once they have been magnetized. This also adds to the overall durability and long-term strength of the magnet.
Neodymium metal can easily fall victim to corrosion or other water and chemical damage. Therefore, the magnets require a protective covering the save them from oxidation and keep up their performance.
· Applications
Due to its immense strength and compact size, the N50 magnets are ideal for multiple purposes. They are used in electric motors and generators due to their high magnetic force. This makes energy generation far more effective and dramatically improves their performance. You can find excellent permanent magnets for your motors on our website.
These magnets are also present in MRI machines that are a crucial part of medical diagnosis and treatment. They are also utilized in aerospace and defense practices since they are components of sensors, magnetic bearings, and actuators, as these need a small size, reliability, and substantial magnetic field to function correctly.
The N50 magnets are also essential parts of speakers and other audio devices. They are crucial for converting electrical signals into sound waves to deliver a superior listening experience. High-frequency magnetic speaker driver units are also available for inquiry.

Magnetic separators require N50 magnets as well to separate magnetic substances from a mixture. This purpose is primarily needed for food processing, mining, and recycling. They are also present in magnetic levitation systems such as maglev trains as they provide contactless levitation of objects that is extremely strong.
N35 Magnets: The Versatile Performers
These are another class of high-energy, neodymium magnets found on the market. The N35 grading on the magnets is a representation of the strength of the magnets. Even with their lesser grading than the N50 magnets, the N35 magnets have many applications where they shine. The average power of N35 magnets is 33 to 37 MGOs.
· Characteristics
Like the N50 magnets, the N35 magnets are potent magnets with a high remanence and good resistance to demagnetization. However, they are less capable when compared to the higher-grade magnets. These are also very susceptible to corrosion and require a coating to safeguard them against this issue. The N35 magnets are comparatively weaker and can break away very quickly if they are not handled with the proper care.
These magnets also display high-temperature resistance, meaning they can maintain their magnetic force's strength even at very intense temperatures. The N35 magnets also have substantial magnetization saturation, making it possible for them to be magnetized to a much greater degree. They can also be magnetized in many ways, such as multipole or axial magnetization.
· Applications
Like the N50 magnets, the N35 magnets are also used in manufacturing electric motors and generators. They are also a component of the Hall effect sensor, industrial control systems, robotics, and your car's electric system. The N35 magnets are also used as clamps and holders, required to keep tools for woodworking and metalworking in place.
These are also the magnets used in the closures for the doors and cabinets around your house, and their sufficient magnetic force keeps these items closed securely. The N35 magnets are also found in the bracelets for magnetic therapy, as magnets are believed to reduce pain and impact blood flow. They are also used in jewelry making for innovative closure methods as they are strong enough to keep the jewelry latches closed but not so strong that it is difficult to open them repeatedly.
Which Magnet Is Stronger – The N35 Or The N50?
As we have already established, the N50 magnets are more substantial and superior to the N35 magnets. The N50 magnets have a higher maximum energy product ad, therefore, a more excellent MGO value when compared to N35 magnets. The reason for the difference in the power between these two magnets is their manufacturing process.
Why Is The N50 Magnet Stronger?
The strength of a magnet is directly related to the density of its magnetic domains and their alignment. The N50 magnets are produced with a superior density of magnetic domains that causes them to have more excellent magnetic when related to the N35 magnets. These magnets are manufactured by subjecting the neodymium metal to strong magnetic fields that cause their domains to align in a particular direction. This leads to the interest in producing very powerful magnetic forces. The N50 magnets are put under more vital magnetic fields than the N35 making them better.
Choosing The Right Magnetic Grade
Selecting the correct magnetic grade for the job is imperative to ensure you get the best and most efficient performance from the chosen magnets. You have to consider many different factors when making your decision:
· Strength And Magnetic Field
You will need to decide how strong of a magnet you require. Evaluate the holding force and magnetic field strength necessary to fulfill the task.
· Operating Conditions
Another point to look into is the environment and conditions the magnet will be needed to work in. Changes in temperature and exposure to corrosive substances such as moisture and chemicals can harm the magnets and lead to demagnetization. Some magnets are less prone to demagnetization and more corrosion-resistant, making them more suitable for use.
· Size And Shape
The size and shape of the magnet are also essential to consider. You will have to decide if the interest will be able to fit where it is required and if it is too thick or thin. You will also have to consider the weight the appeal will have to withstand, as some are more brittle than others.
· Cost
The higher the grade of the magnet, the more expensive it is. Decide the magnets and strength you need and balance them with your budget.
· Availability
Neodymium magnets such as the N50 and N35 magnets are readily available on the market. However, higher-grade magnets are more challenging to find and can take much longer to source. Look into the availability of the required grade to ensure it can be found within the time limits of your projects.
· Magnetic Stability
Some magnets are more likely to hold on to magnetic force for extended periods making them more stable. Check the magnet's stability against how long you need them to function.
· Safety Concerns
These strong can interfere with the performance of other electronic devices, making them a safety hazard. They can even affect pacemakers, and if strong enough, they can attract magnetic materials toward them at high speeds and seriously injure anyone in their path.
· Expert Consultation
You can always turn to experts to help you decide what grade you should go with. Magnet suppliers and manufacturers have in-depth knowledge of the properties of magnets and what the different grades are capable of. Discussing will help you choose the best magnet to fulfill all your requirements.
Conclusion
You now better understand how magnets are graded and the factors involved in determining magnet grades. We have also discussed the different characteristics of the N35 and N50 magnets and what makes the N50 magnets superior. There are also multiple applications for these magnets. Hopefully, you now know all the factors that must be considered when choosing a magnet grade and the reasons behind them. Hopefully, you will now be able to easily select the right magnet to meet all the requirements you have for your application.